Visibility is the first step in effective security monitoring. That’s why it is no surprise that intrusion detection systems (IDS) have become an incredibly popular first line of defense for many organizations around the world.
This guide provides an introduction to IDS types, detection methods, and alerts while also highlighting alternative means of network security that might benefit organizations looking for IDS detection without IDS challenges.
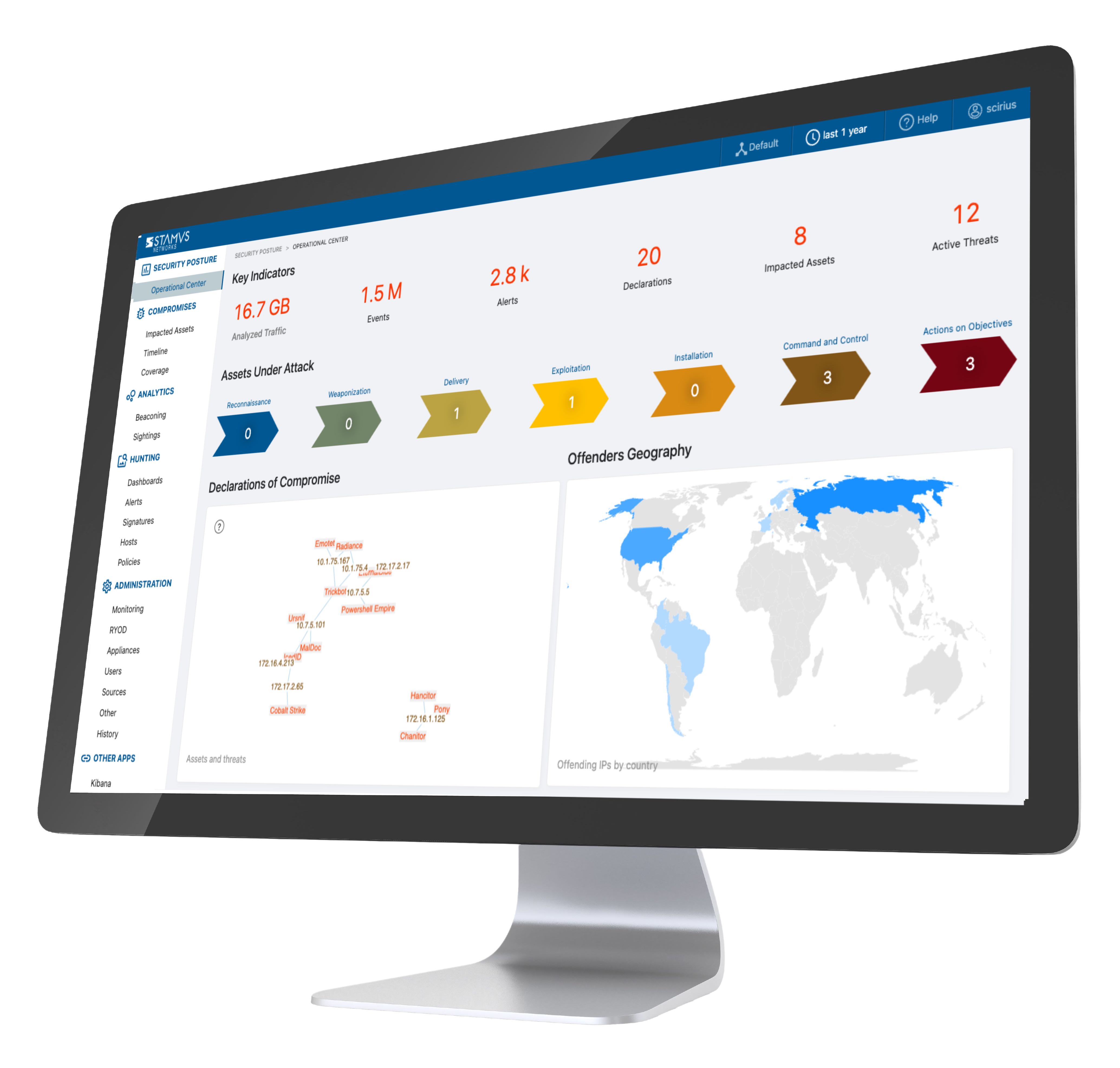
An intrusion detection/prevention system in cyber security is a security mechanism employed to safeguard computer networks and systems from unauthorized access and malicious activity. Both IDS and IPS are commonly used as a first line of defense for many organizations. Intrusion detection techniques often include monitoring traffic, comparing traffic to a set of predefined rules or signatures, and then issuing alerts when traffic matches a malicious pattern.
Intrusion detection usually concentrates on identifying and reporting potential security breaches, while intrusion prevention seeks to actively block threats. Early detection of intrusions allows security teams to take action and minimize damage. This can involve isolating infected devices, blocking attackers, or launching incident response procedures.
The difference between IPS and IDS is that IPS actively blocks threats while IDS simply provides alerts. Both systems serve a purpose in an organization’s strategy and come with their own benefits and challenges.
There are two main types of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) based on their deployment and data source:
1. Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS): NIDS act as network monitoring devices deployed at strategic points within a computer network. Their primary function is to continuously capture and analyze network traffic data traversing a specific network segment. NIDS can be implemented in two primary ways:
NIDS typically utilizes network adapter promiscuous mode. This mode allows the NIDS to capture all network traffic on the attached network segment, regardless of its intended recipient. NIDS employs two main techniques for analyzing captured network traffic data: signature-based detection and anomaly-based detection.
2. Host-Based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS): In contrast to NIDS which focuses on network traffic analysis, HIDS provides security for individual devices (hosts) within the network. HIDS function as software agents deployed directly on the operating system of the host device itself. Their primary function is to monitor and analyze activity occurring on the host device. HIDS are deployed as software agents on individual servers, desktops, or laptops within the network. A single HIDS agent is typically installed on each host device for dedicated monitoring.
HIDS collects data from various sources on the host device, including:
HIDS primarily utilizes anomaly-based detection techniques. By analyzing the collected data, HIDS establishes baselines for typical host activity. Significant deviations from these baselines, such as unusual file access attempts or unexpected processes running, can indicate potential intrusions or suspicious behavior.
There are three primary methods of IDS/IPS detection: anomaly-based, signature-based, and hybrid. These methods define how the IDS analyzes data to identify potential intrusions.
Each of these three detection methods (Anomaly-based, Signature-based, Hybrid) offers different strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the most suitable approach depends on factors like the specific security requirements of the network, the resource availability for managing the IDS, and the acceptable level of false positives.
It is also important to consider switching to a more advanced modern network security solution, such as network detection and response (NDR). The Stamus Security Platform (SSP) is a modern NDR solution that leverages the best from IDS technology without the same challenges faced by IDS users. Learn more at https://www.stamus-networks.com/stamus-security-platform
The most common detection method used by an IDS is signature-based detection.
Here's why:
However, it's important to note that signature-based detection has limitations:
IDS alerts can be categorized based on their accuracy in reflecting actual threats. There are four main types of IDS alerts regardless of the type of intrusion detection system:
An IDS can detect a wide range of computer attacks by analyzing network traffic or system activity for suspicious patterns. Here are some common types of intrusions in cybersecurity that IDS systems are designed to identify:
It's important to remember that IDS effectiveness depends on its configuration and the type of attack. While some attacks leave clear signatures, other more subtle attack signals such as homoglyphs and C2 beaconing are likely to be missed. That is why it is important to consider switching from IDS to a modern network detection and response (NDR) platform to make sure critical attack signals don’t fly under the radar.
The three main methods used when evaluating IDS for effectiveness are the detection/false positive rate, false negative/time to detect rate, and scenario-based testing. Let’s take a look at each:
1. Detection Rate and False Positive Rate:
This method focuses on the IDS's ability to accurately identify true threats. It involves analyzing two key metrics:
Evaluating these metrics together helps assess the trade-off between catching threats and generating false alarms. A good IDS should have a high DR and a low FPR.
2. False Negative Rate and Time to Detection:
This method focuses on the speed and accuracy of the IDS in identifying threats. It involves analyzing two additional metrics:
Evaluating these metrics helps assess the IDS's responsiveness and ability to minimize the window of opportunity for attackers.
3. Scenario-Based Testing:
This method involves simulating real-world attack scenarios against the IDS. This can be done using pre-recorded attack data or specialized testing tools. Scenario-based testing helps assess the IDS's effectiveness against various attack types and its ability to adapt to evolving threats.
By combining these three methods, security professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of an IDS's strengths and weaknesses, allowing them to choose the most suitable solution for their specific needs.
IDS is undoubtedly a powerful and effective means to detect known threats on your organization’s network. Unfortunately, most IDS deployments are riddled with false positives, provide limited threat detection, and lack sufficient visibility into anomalous activity and subtle attack signals. Traditional IDS vendors have failed to innovate in ways that solve these challenges, leading to inefficient or downright ineffective threat detection.
You need a network security platform that doesn’t generate an endless stream of useless alerts across part of your network, and instead automatically identifies alerts of interest and notifies you of only serious and imminent threats. Your organization deserves response-ready detection with visibility into your entire network regardless of the environment with easy access to all the contextual evidence you need to stop an attack before it can cause damage. Replace your legacy IDS with a modern network detection and response platform that gives you these features and more.
The Stamus Security Platform™ is a network-based threat detection and response solution that eliminates the challenges of legacy IDS while lowering your response time. Stamus Security Platform harnesses the full potential of your network, bringing state-of-the-art threat detection, automated event triage, and unparalleled visibility to the security team.
Book a demo to see if Stamus Security Platform is right for your organization.
If you're considering upgrading from IDS to a modern alternative, we recommend looking at the following resources.
ABOUT STAMUS NETWORKS ™
Stamus Networks believes that cyber defense is bigger than any single person, platform, company, or technology. That’s why we leverage the power of community to deliver the next generation of open and transparent network defense. Trusted by security teams at the world’s most targeted organizations, our flagship offering – Clear NDR™ – empowers cyber defenders to uncover and stop serious threats and unauthorized network activity before they harm their organizations. Clear NDR helps defenders see more clearly and act more confidently through detection they can trust with results they can explain.
© 2014-2025 Stamus Networks, Inc. All rights Reserved.